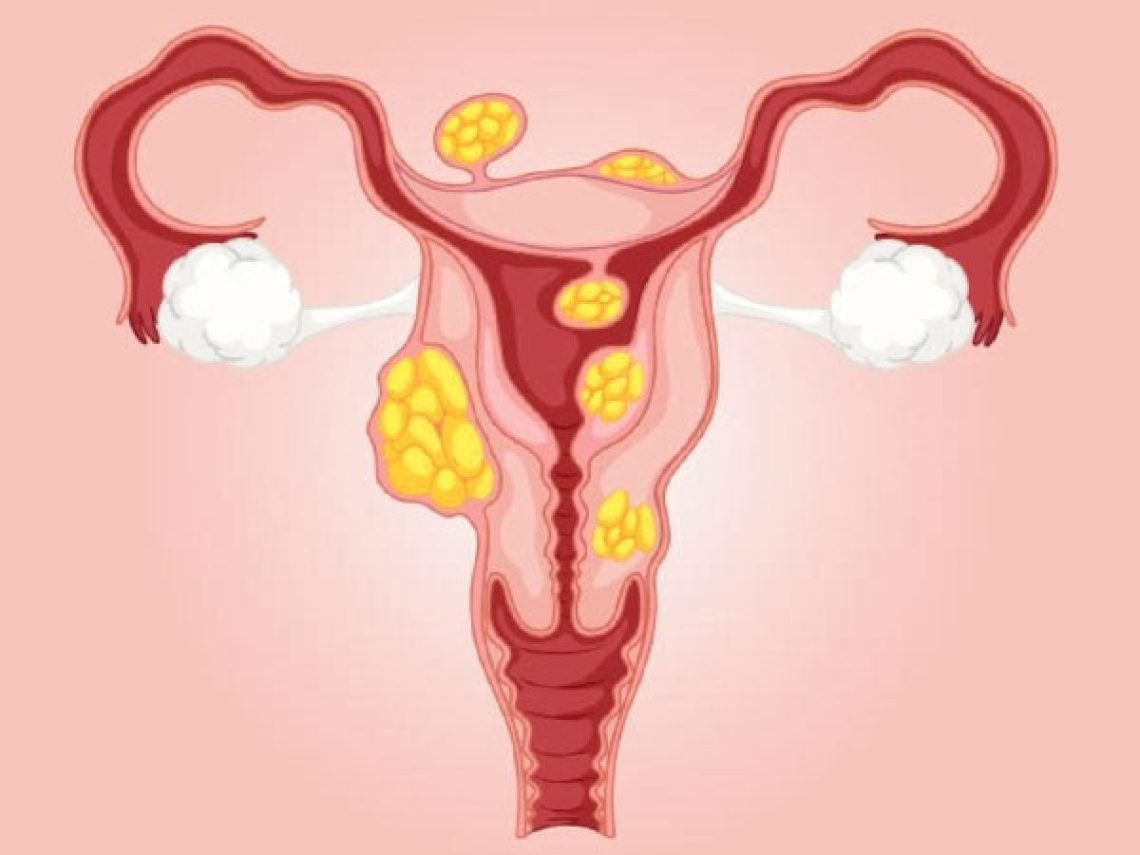
Fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus, affecting many women during their reproductive years. Submucosal fibroids are a specific type of fibroid that can cause various symptoms and impact a woman’s quality of life. In this blog, we’ll delve into what submucosal fibroids are, their symptoms, how they are diagnosed, and the available treatment options.
What are Submucosal Fibroids? A submucosal fibroid is a benign tumor that develops in the inner layer of the uterus, known as the endometrium. Unlike intramural fibroids, which grow within the muscular wall of the uterus, or subserosal fibroids, which protrude outward from the uterine wall, submucosal fibroids extend into the uterine cavity. This positioning can lead to more pronounced symptoms and complications.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of Submucosal Fibroids:
Submucosal fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Prolonged menstrual periods
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Pelvic pain and pressure
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
- Iron deficiency anemia due to excessive blood loss
These symptoms can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life, affecting her physical, emotional, and social well-being.
Diagnosis of Submucosal Fibroids
Diagnosing submucosal fibroids typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests. Your healthcare provider may perform:
- Pelvic examination: A doctor may feel for abnormalities in the uterus during a pelvic exam.
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound or pelvic ultrasound can provide detailed images of the uterus, allowing healthcare providers to visualize the size, location, and number of fibroids.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans offer more detailed images than ultrasound and can help differentiate between different types of fibroids and identify their precise location within the uterus.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for submucosal fibroids depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the patient’s reproductive plans. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or hormonal medications such as birth control pills or hormonal IUDs may help alleviate symptoms such as heavy bleeding and menstrual pain.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Procedures such as hysteroscopic myomectomy involve removing fibroids through the cervix using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube with a camera.
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): This minimally invasive procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- Surgical Removal: In some cases, particularly if the fibroids are large or causing severe symptoms, surgical options such as a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended.
Conclusion
Submucosal fibroids can significantly impact a woman’s health and quality of life, leading to symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and discomfort during intercourse. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications. If you experience any symptoms suggestive of submucosal fibroids, consult with your healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan. With advances in medical technology and treatment options, women with submucosal fibroids can find relief and improve their overall well-being.